Product Description
elevator Rack Actuator railway axle Automatic Window Opening System Custom Engineering Construction Hoist Rack And Pinion Elevator Lifting Gear Rack
|
Product name |
Gear rack |
|||
|
Type |
Helical gear rack,spur gear rack,sliding gate gear rack |
|||
|
Module |
M1,M1.5,M2,M2.5,M3,M4,M5,M6,M8,M10 |
|||
|
Precision |
DIN6,DIN7,DIN8,DIN9 |
|||
|
Surface treatment |
Black oxide,zinc galvanize, heat treatment, |
|||
|
Material |
Carbon steel,stainless steel,brass,pom,nylon,plastic |
|||
|
Process method |
CNC machining, Turning, milling ,drilling, grinding,shaving,shaping,hobbing |
|||
|
Application |
Automotive Parts,Hareware Par,Construction,Machinery, |
|||
|
Standard |
ISO |
|||
Related products
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Installation Guide |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1.5 Years |
| Type: | Gear Rack |
| Application: | Excavator |
| Certification: | CE, ISO9001: 2000 |
| Condition: | New |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
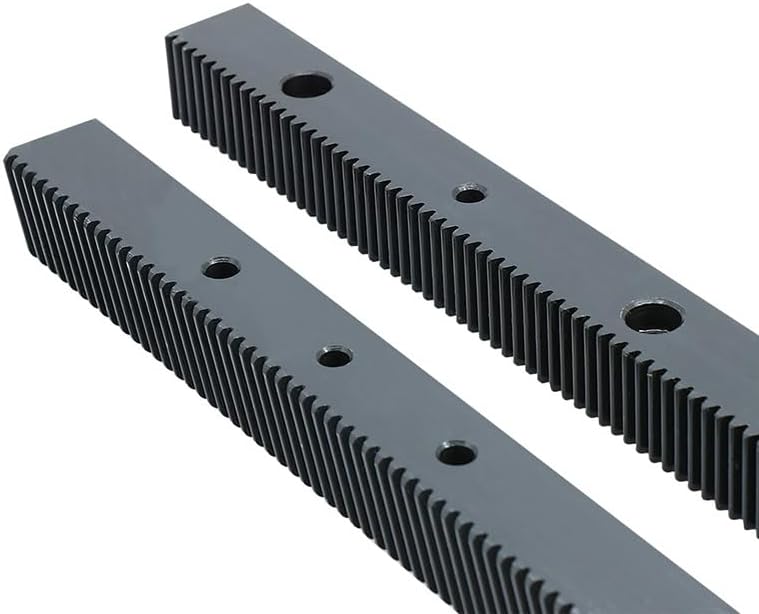

How do metric gear racks handle different gear ratios?
Metric gear racks are not directly involved in handling different gear ratios. Gear ratios are determined by the combination of gear racks with other gears, such as spur gears, helical gears, or bevel gears. However, metric gear racks play a crucial role in the overall gear system and contribute to achieving the desired gear ratio. Here’s a detailed explanation of how metric gear racks interact with other gears to handle different gear ratios:
1. Gear Rack Basics: A gear rack is a linear toothed component with straight teeth that meshes with a gear. Unlike traditional gears that rotate, gear racks provide linear motion. They are often used in conjunction with other gears to convert rotational motion into linear motion or vice versa. Gear racks typically have teeth cut along one edge, and these teeth engage with the teeth of the mating gear to transmit power and motion.
2. Spur Gear Systems: One common configuration is to use a spur gear in combination with a gear rack to achieve a specific gear ratio. A spur gear is a cylindrical gear with straight teeth that mesh with the teeth of the gear rack. The gear ratio in this system is determined by the number of teeth on the gear and the length of the gear rack. By selecting gears with different numbers of teeth or using gear racks of varying lengths, different gear ratios can be achieved. The gear ratio is calculated as the ratio of the number of teeth on the gear to the length of the gear rack.
3. Helical Gear Systems: In helical gear systems, helical gears with angled teeth are often used in conjunction with gear racks. Helical gears offer advantages such as smoother operation and increased load-carrying capacity compared to spur gears. The gear ratio in a helical gear system is determined by the number of teeth on the gear and the pitch of the helical gear. The gear rack meshes with the helical gear at a specific angle, and as the gear rotates, it translates the rotational motion into linear motion along the gear rack.
4. Bevel Gear Systems: Bevel gear systems involve the use of bevel gears, which have conical-shaped teeth, to transmit motion between non-parallel shafts. While gear racks are not typically used directly in bevel gear systems, they can be incorporated in conjunction with other gears to achieve specific motion requirements. For example, a bevel gear system may use a combination of bevel gears and gear racks to transmit motion and adjust the gear ratio between intersecting or perpendicular shafts.
It is important to note that the gear ratio achieved in a gear system is not solely determined by the gear rack itself but by the combination of gears and their respective sizes, tooth counts, and profiles. The gear rack’s length or the number of teeth on the rack may influence the overall gear ratio, but it is the interaction between the gear rack and the mating gear that determines the specific ratio achieved.
In summary, metric gear racks are integral components in gear systems that involve the conversion of rotational motion to linear motion or vice versa. They work in conjunction with other gears, such as spur gears, helical gears, or bevel gears, to achieve the desired gear ratio. By selecting gears with different tooth counts and combining them with appropriate gear racks, engineers can design gear systems that handle different gear ratios to meet specific application requirements.

Can metric gear racks be used for both rotary and linear motion?
Yes, metric gear racks can be used for both rotary and linear motion. Here’s a detailed explanation of how metric gear racks can be utilized for these types of motion:
1. Linear Motion: Gear racks are primarily designed to provide linear motion. A gear rack consists of straight teeth that are cut along one edge of a linear component. The teeth of the gear rack mesh with the teeth of a mating gear, typically a spur gear or a helical gear. As the mating gear rotates, it engages with the gear rack and translates the rotational motion into linear motion. This linear motion can be used in various applications, such as in machinery, automation systems, robotics, and conveyors, where linear movement is required.
2. Rotary Motion: While gear racks are primarily used for linear motion, they can also be adapted for rotary motion in specific scenarios. One common method is by using a pinion gear, which is a small gear with teeth that mesh with the gear rack. The pinion gear is mounted on a rotating shaft, and as it engages with the gear rack, it converts the linear motion of the rack into rotary motion of the shaft. This configuration is often used in applications where a linear actuator or a rack and pinion mechanism is required to transform linear motion into rotational motion or vice versa. Examples include steering systems in automobiles, CNC machines, or rack and pinion lifts.
It is important to note that while gear racks can be used for both rotary and linear motion, their primary purpose is to provide linear motion. Rotary motion is achieved by incorporating additional components, such as pinion gears or other types of gears, to convert the linear motion of the gear rack into rotational motion. The specific design and configuration depend on the application requirements and the desired motion transformation.
In summary, metric gear racks are versatile components that can be used for both linear and rotary motion. Their primary function is to provide linear motion when meshed with a mating gear. However, by incorporating pinion gears or other gears, the linear motion of the gear rack can be transformed into rotary motion. This flexibility allows engineers to utilize gear racks in a wide range of applications where both types of motion are required.
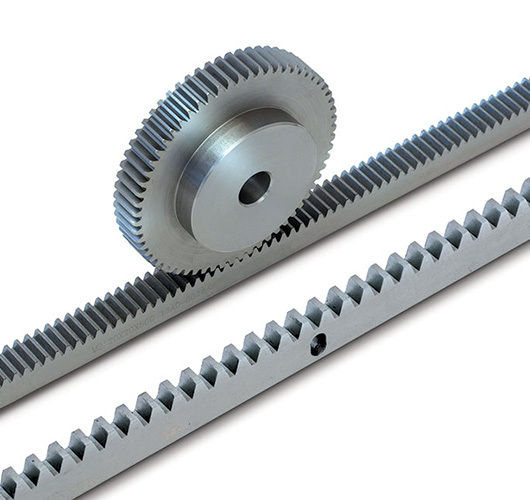
How does a metric gear rack differ from other types of gear racks?
A metric gear rack differs from other types of gear racks in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between a metric gear rack and other types of gear racks:
1. Measurement System: The primary difference lies in the measurement system used for defining the gear rack dimensions. A metric gear rack follows the metric system of measurement, where the module represents the size of the gear teeth. In contrast, other types of gear racks, such as inch gear racks, use the inch-based system of measurement, where the diametral pitch or circular pitch is used to specify the gear tooth size. The use of different measurement systems distinguishes metric gear racks from other types of gear racks.
2. Tooth Profile: Metric gear racks typically have a straight-sided tooth profile, known as the involute profile. This tooth profile is widely used in metric gear systems and ensures smooth and efficient tooth engagement with mating gears or pinions. In contrast, other types of gear racks may have different tooth profiles based on the specific gear system they are designed for. For example, inch gear racks may use tooth profiles such as the circular or diametral pitch profile. The tooth profile variations differentiate metric gear racks from other types of gear racks.
3. Standardization: Metric gear racks benefit from a higher degree of standardization compared to other types of gear racks. The metric system is widely adopted and standardized in many countries and industries, promoting compatibility and interchangeability of metric gear rack components. This standardization simplifies the selection, integration, and replacement of metric gear racks in machinery. On the other hand, other types of gear racks may have variations in tooth profiles, dimensions, and standards, leading to less universal compatibility and interchangeability.
4. Application Areas: Metric gear racks are commonly used in industries and countries where the metric system is prevalent. They find extensive application in machinery and equipment designed and manufactured based on metric specifications. Other types of gear racks, such as inch gear racks, are typically used in regions or industries where the inch-based measurement system is more prevalent. The choice of gear rack type depends on the specific application requirements and the measurement system adopted in the target market.
5. Availability: Due to the widespread adoption of the metric system in many countries, metric gear racks are generally more readily available in the market compared to other types of gear racks. There is a wide range of metric gear rack options offered by various manufacturers, providing greater accessibility and availability for machinery designers and manufacturers. However, the availability of other types of gear racks may vary depending on the specific region or industry where they are commonly used.
While the measurement system, tooth profile, standardization, application areas, and availability differentiate metric gear racks from other types of gear racks, it’s important to note that the fundamental purpose of all gear racks remains the same – to provide linear motion, precise positioning, and motion control in machinery and mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2024-04-17